Introduction
The European Union (EU) contains a comprehensive law known as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) that lays out strict guidelines for the gathering, handling, and archiving of personal data about individuals. On May 25, 2018, the GDPR came into force, and since then, it has changed how businesses handle and protect customer data. In this article, we'll look at the different GDPR principles and discuss their relevance in the modern digital environment.
The Fundamental Principles of GDPR: A Deep Dive
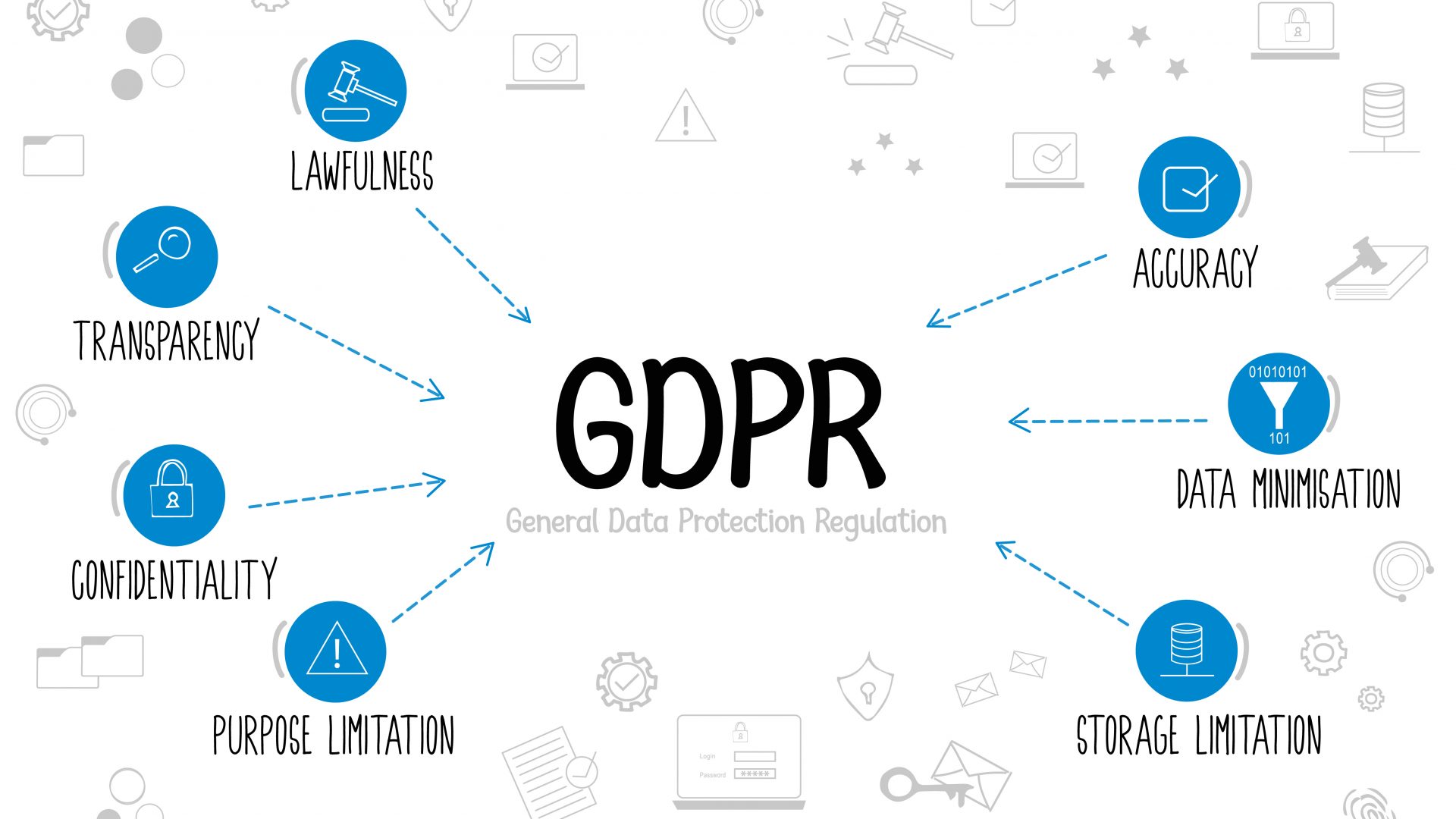
The GDPR has six key principles that form the foundation of the regulation. These principles are:
- Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
- Purpose Limitation
- Data Minimization
- Accuracy
- Storage Limitation
- Integrity and Confidentiality
Let's have a closer look at these principles.
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
Organizations must process personal data lawfully, fairly, and transparently. They must disclose personal data to individuals and have a legal justification for collecting and processing it. They also need to let people know what will be done with their personal information, who will get it, and how long it will be kept.
Purpose Limitation
The principle of purpose limitation states that personal data must be collected for specific, explicit, and lawful purposes and may not be used for any other purpose. Companies must give consumers a clear explanation of why they are collecting their personal information and must not use that information for any other purpose without that person's consent.
Data Minimization
According to the data minimization principle, companies must only gather the personal information required for the particular purposes for which it was collected. Companies must avoid gathering excessive amounts of personal data since doing so might compromise individual's security and privacy.
Accuracy
Companies must adhere to the accuracy principle by making sure that the personal data they collect and use is accurate and up-to-date. They must immediately update or delete any inaccurate personal data by taking all necessary precautions.
Storage Limitation:
According to the storage limitation principle, businesses must keep personal data for the particular purposes for which it was collected. Companies must also put in place the necessary security measures to guarantee the safe storage of individuals information.
Integrity and Confidentiality:
The integrity and confidentiality principle requires companies to safeguard consumer data from unlawful access, modification, or disclosure. Additionally, businesses must have the appropriate organizational and technical measures in place to guarantee the privacy, integrity, and availability of personal data.
Accountability
To ensure their compliance with the GDPR, which places a strong emphasis on accountability, organizations must take proactive measures. Companies must therefore be able to demonstrate that they have implemented the required security measures to safeguard the personal data they collect, use, and retain.
FAQs on GDPR Principles: Clarifying the Confusions
What is personal data under the GDPR?
Personal data is any information identifying a living individual. Additionally, this covers less delicate information like names, addresses, phone numbers, emails, and IP addresses as well as more sensitive information like racial or ethnic origin, political beliefs, religious views, and union membership.
Who is responsible for ensuring GDPR compliance?
GDPR compliance is the responsibility of the Data Controller, or the business that decides the roles and procedures for processing personal data. The organization that processes personal data on behalf of the Data Controller is known as the Data Processor.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with the GDPR principles?
Non-compliance with the GDPR imposes severe penalties, including fines of up to 4% of an organization's annual global sales or €20 million (whichever is higher). Additionally, corporations may be held responsible for any losses caused by a data breach.
What are the rights of individuals under the GDPR?
Under the GDPR, individuals have several rights regarding their personal data, including the right to:
- Access their data.
- Request correction of their data.
- Request erasure of their data.
- Object to the processing of their data.
- Request restriction of processing their data.
- Request a copy of their data in a commonly used format (data portability).
- Lodge a complaint with the supervisory authority.
What is the role of the Data Protection Officer (DPO)?
The Data Protection Officer (DPO), who is in charge of managing a company's GDPR compliance operations, makes sure the business complies with data protection laws. The DPO also offers advice on all issues pertaining to data protection. According to the GDPR, a corporation must employ a DPO if it processes a significant amount of personal data, does routine person monitoring, or handles sensitive data.
Protect Your Business and Customers Today with Sovy's Data Privacy Essentials Solution. Start Now and Adhere to GDPR Fundamentals with Confidence!
Last updated: January 2, 2023


 To make this site work properly, sometimes we place small data files called cookies on your device. This is a common practice for websites.
To make this site work properly, sometimes we place small data files called cookies on your device. This is a common practice for websites.